The Science of Food Synergy: How Strategic Food Combinations Boost Your Health
Your body is like a complex orchestra, and the foods you eat are the instruments. While each food has its own nutritional melody, the real magic happens when you combine certain foods together, creating powerful harmonies that amplify their health benefits far beyond what they could achieve alone. This fascinating phenomenon is called food synergy, and understanding it can transform how you approach nutrition.
What Is Food Synergy?
Food synergy occurs when combining specific foods creates enhanced health benefits that exceed the sum of their individual parts. This happens through various mechanisms: one food may increase the absorption of nutrients from another, protect beneficial compounds from breaking down, or work together to target the same health concern more effectively.
The concept is rooted in solid science. Your immune system and overall health depend not just on getting adequate nutrition, but on how well your body can actually use those nutrients. This is where strategic food pairing becomes a game-changer.
Powerful Food Combinations for Enhanced Immunity
Green Tea + Black Pepper + Lemon: The Triple Threat
This combination creates one of the most potent antioxidant boosters you can easily incorporate into your daily routine. Black pepper contains piperine, which dramatically slows down the breakdown of EGCG (the primary antioxidant in green tea) in your digestive system, allowing your body more time to absorb it. Add lemon to this mix, and the vitamin C increases antioxidant absorption by an incredible ten-fold compared to drinking green tea alone. The vitamin C and catechins work together synergistically, making this combination a powerhouse for immune support and disease prevention.
Turmeric + Black Pepper: Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Perhaps no food combination is more scientifically validated than turmeric and black pepper. The piperine in black pepper increases curcumin bioavailability by up to 1000 times by preventing its rapid breakdown in the liver and gut. This means your body can actually use turmeric's powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer compounds instead of simply eliminating them. For maximum benefit, add turmeric and black pepper to dishes containing healthy fats, as curcumin is fat-soluble.
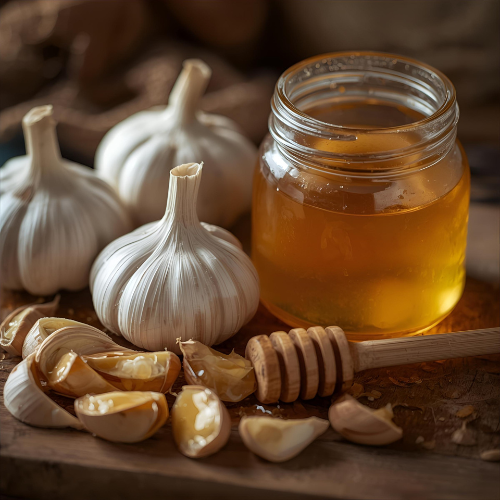
Garlic + Honey: Nature's Antibiotic Duo
This traditional remedy has serious scientific backing. When garlic reaches your stomach, it stimulates gastric juice production, which enhances iron absorption and enriches your bloodstream. Meanwhile, both garlic and honey contain phenols and fatty acids that work together to create potent antibacterial effects, far exceeding what either could achieve alone. This combination also helps improve the shelf life of foods naturally.
Maximizing Nutrient Absorption Through Smart Pairing
Iron Absorption Champions: Vitamin C + Iron-Rich Foods
If you're concerned about iron deficiency, this pairing is crucial. Vitamin C converts non-absorbable iron into a form your body can readily use. Squeeze lemon over spinach, add bell peppers to lentil dishes, or pair strawberries with red meats. This combination is particularly important for vegetarians and women with higher iron needs.
Carotenoid Maximizers: Eggs + Colorful Vegetables
Adding eggs to your salad isn't just for protein, it's a smart absorption strategy. The healthy fats in egg yolks help your body absorb fat-soluble carotenoids like lycopene, lutein, and beta-carotene from tomatoes, carrots, and leafy greens by 3-9 times more effectively. These compounds are crucial for eye health, immune function, and disease prevention.
Probiotic + Prebiotic Power: Yogurt + Bananas
Your gut health affects everything from immunity to mood, making this combination particularly valuable. Yogurt provides beneficial bacteria (probiotics), while apples, berries or bananas supply inulin, a prebiotic fiber that feeds and energizes these good bacteria. This partnership improves digestion, enhances immunity, and even increases calcium absorption in your body.
Disease-Fighting Food Combinations
Heart Health Heroes
Tomatoes + Olive Oil
The fat in olive oil dramatically increases absorption of lycopene from tomatoes – and cooking tomatoes increases their lycopene content by 5-6 times. This combination provides powerful cardiovascular protection through improved lipid profiles and reduced inflammation.
Garlic + Fish
This pairing provides complementary omega-3 fatty acids and compounds that work together to reduce inflammation, lower cholesterol, and support heart health through multiple pathways
Onions + Grapes
An unexpected but powerful combination that inhibits blood clot formation and provides synergistic cardiovascular protection through their combined polyphenol content.
Blood Sugar Support
Apple Cider + Blueberry Juice
Research shows an 80:20 ratio of apple cider to blueberry juice provides optimal anti-hypertensive and anti-hyperglycemic properties.
Onions + Garlic
Both contain compounds that stimulate insulin production and help control blood glucose levels, making this combination particularly beneficial for diabetes management.
Cancer Prevention Pairs
Apples with Skin + Berries
The diverse phytochemicals in this combination work together to enhance DNA repair and reduce oxidative damage that can lead to cancer cell formation.
Broccoli + Tomatoes
This combination shows remarkable anti-tumor properties, with studies demonstrating significantly slower prostate tumor growth when both foods are consumed together rather than separately.
Mental Health and Cognitive Function
Apples + Leafy Greens
The flavonoids in apples combined with dietary nitrates in greens increase nitric oxide production, which can improve cognitive function and mood.
Blueberries + Strawberries
This antioxidant-rich combination reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain, improving neuronal signal processing and cognitive function.
Practical Tips for Implementing Food Synergy
Start Simple: Begin with one or two combinations that appeal to you and fit easily into your current eating patterns.
Think Beyond Single Meals: You don't need to eat synergistic foods in the same bite. Consuming them within the same meal or day can still provide benefits.
Cook Smart: Remember that some combinations work better when cooked (like tomatoes and olive oil), while others are best raw (like vitamin C sources with plant-based iron-rich foods).
Season Strategically: Use herbs and spices not just for flavor, but for their synergistic properties. Adding black pepper to turmeric-spiced dishes, or rosemary to grilled meats, provides both taste and health benefits.
Focus on Whole Foods: While supplements have their place, food synergy works best with whole, minimally processed foods that contain the full spectrum of beneficial compounds.
The Bottom Line
Food synergy represents a shift from thinking about individual nutrients to understanding food as complex systems of interacting compounds. By strategically combining foods, you can dramatically increase your body's ability to absorb and use the nutrients you consume, leading to better health outcomes with the same or even fewer total calories.
The beauty of food synergy lies in its accessibility, these aren't exotic superfoods or expensive supplements, but simple combinations of everyday ingredients that can transform your health from the inside out. Start experimenting with these combinations today, and let your body experience the powerful difference that food synergy can make.
Remember: While food synergy can significantly enhance nutrition, it's not a replacement for overall healthy eating patterns. Information contained in this post is for educational purposes only and does not replace the advice of your qualified health care professional. Always consult with healthcare providers for personalised nutritional advice, especially if you have specific health conditions or take medications and supplements.
Read the full paper here:
https://journalofethnicfoods.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s42779-019-0033-3